CISCO CWDM SOLUTION APPLICATIONS
The Cisco CWDM solution based on CWDM gigabit interface converters (GBICs) and Small Form-Factor Pluggables (SFPs) and passive modules allows enterprise companies and service providers to provide scalable and easy-to-deploy Gigabit Ethernet and Fibre Channel services in their networks. The product set helps enable the flexible design of highly available and scalable multiservice networks.
The Cisco CWDM GBIC SFP solution is a convenient and cost-effective solution for the adoption of Gigabit Ethernet and Fibre Channel in campus, data-center, and metropolitan-area access networks.
Because of the flexibility of the passive devices, Cisco CWDM solution helps enable the deployment of a variety of topologies to multiplex up to eight different wavelengths on the same pair of fibers in protected or unprotected configurations. A connection between two endpoints is protected when it is associated with two channels (typically of the same wavelength) traveling on diverse fiber routes (for example, clockwise and counterclockwise in ring configurations or on separate fibers in point-to-point scenarios). Single-wavelength OADMs are equipped with two channels traveling different network paths (east and west) to offer redundancy or protection in rings. On the other hand, because CWDM-MUX8A= and CWDM-OADM4-x= have only a single network port (that is, one fiber path), two CWDM-MUX8A= or two CWDM-MUX4-x= are required to connect to redundant (protected) fiber routes.
Figures 2 through 11 illustrate the numerous protected and unprotected deployment scenarios of the Cisco CWDM solution with the Cisco WDM(DS-SFP-FC4G-SW) series of passive devices. The following conventions are adopted in the figures:
• Colored circles represent transceivers (GBIC or SFP) at the corresponding color-coded wavelength connected to the filter equipment port.
• N indicates the network port on the CWDM-MUX8A= and CWDM-OADM4-x=.
• P indicates the pass port on the part number CWDM-OADM4-x=.
• E and W indicate the network east and network west ports on the CWDM-OADM1-xxxx=.
Figure 2. Point-to-Point Configurations with 4- and 8-Channel Passive Devices
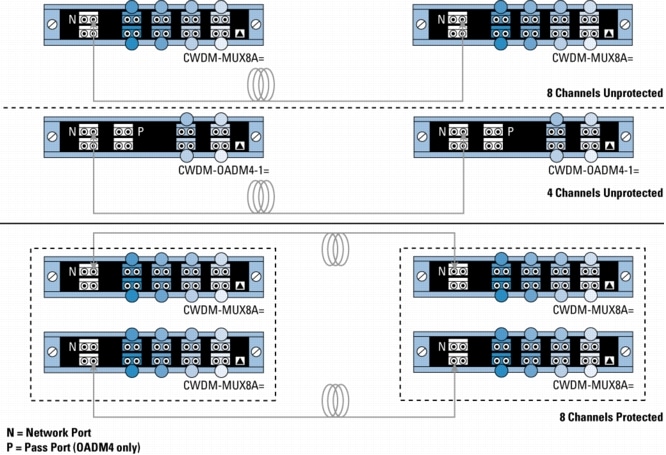
Figure 3. Point-to-Point Configuration with 4-Channel OADMs and Regeneration
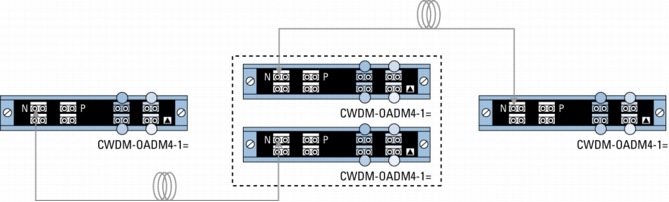
Figure 4. Unprotected Bus Configurations with 4- and 1-Channel OADMs With and Without Regeneration
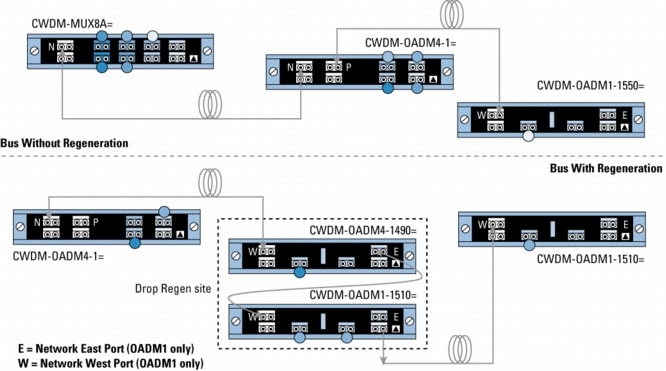
Figure 5. Protected Hub-and-Spoke Configuration with 8-Channel Multiplexer/Demultiplexer and 4-Channel OADMs
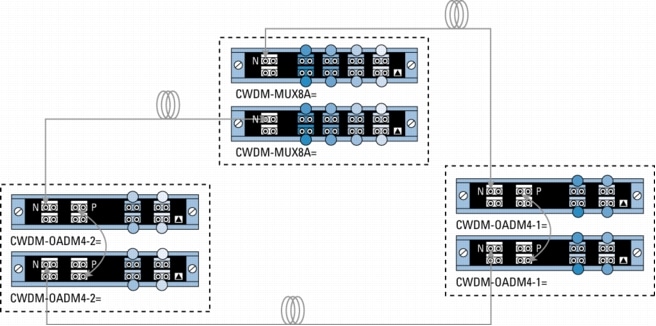
Figure 6. Protected Hub-and-Spoke Configuration with 8-Channel Multiplexer/Demultiplexer and 4- and 1-Channel OADMs
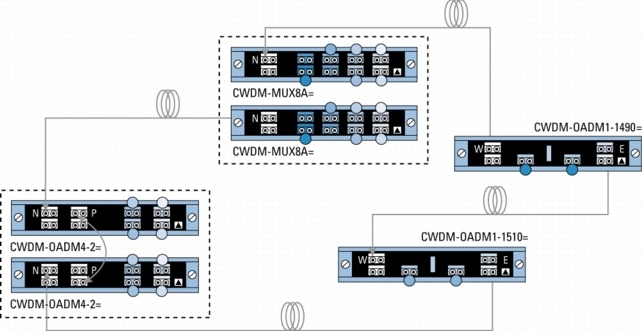
Figure 7. Protected Meshed-Ring Configuration with 4- and 1-Channel OADMs
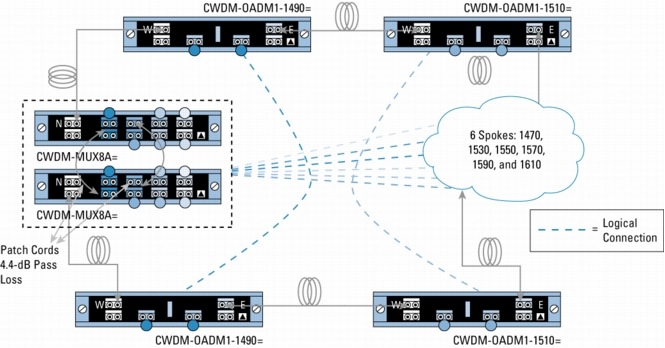
Figure 8. Protected Meshed-Ring Configuration with 8-Channel Multiplexer/Demultiplexer and 1-Channel OADMs
Figure 9. Mixing 1300-nm and CWDM in Point-to-Point Configuration with 1300-nm OADM Transparency
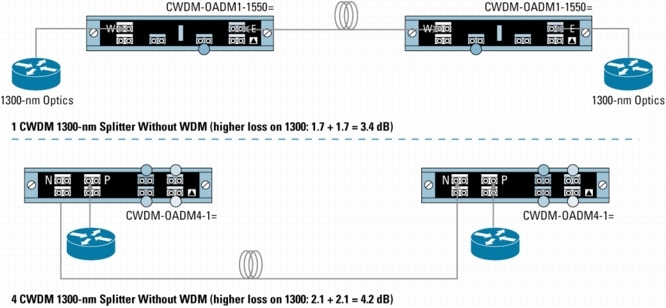
Figure 10. Mixing 1300-nm and CWDM in Point-to-Point Configuration with WDM Splitter Cable
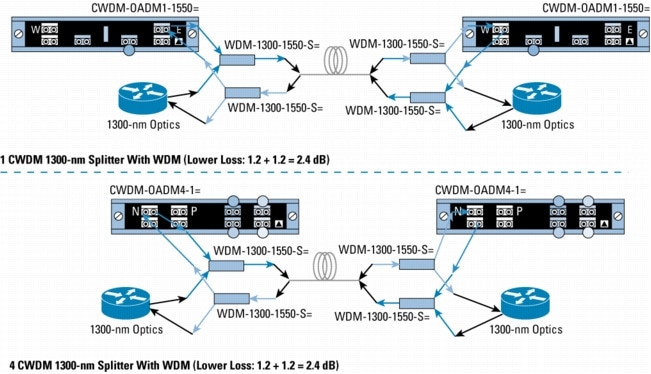
Figure 11. Mixing 1300-nm and CWDM in Protected Rings with WDM Splitter Cable
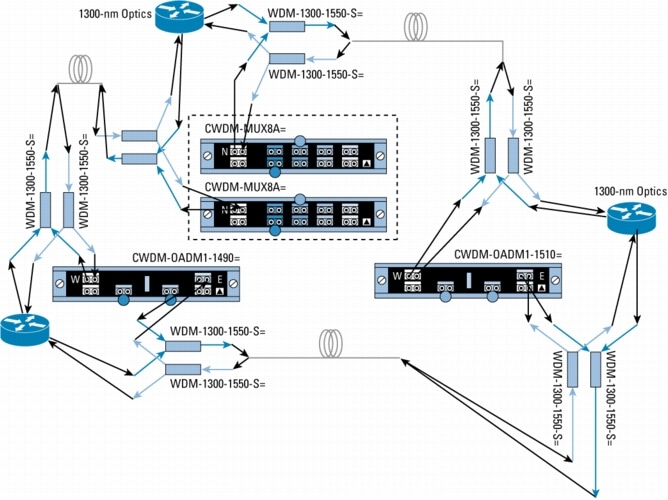
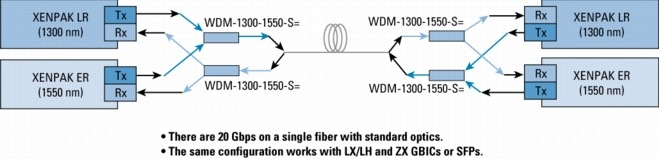
Figure 12. WDM Splitter Cable for Non-CWDM Applications
No comments:
Post a Comment